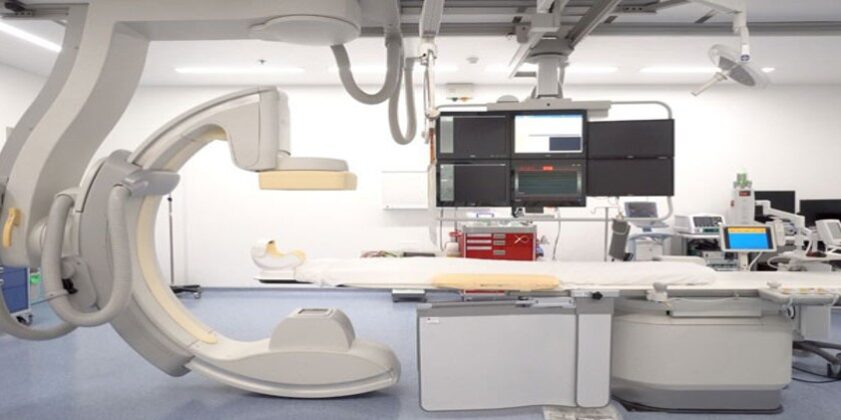
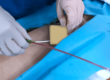
A Catheterization Laboratory is an examination room at a medical facility. These labs are utilized by interventional cardiologists, nurses, and trained technicians to perform minimally invasive procedures for the diagnosis and treatment of cardiac issues.
Diagnostic imaging equipment in cath labs is used to visualize the arteries and the heart and treat abnormalities in the heart. This is done by creating a small puncture site in a large artery in the body and inserting a thin, hollow tube, called a catheter to detect abnormalities.
General puncture types:
1.Femoral route
In this route, the targeted artery is the Common Femoral artery (a continuation of the External Iliac artery) with a diameter of 4mm to 9mm. The location of the puncture site is in the groin area, parallel to the femur bone.

2.Radial route
The targeted artery in this route is the Radial artery (a continuation of Brachial artery) with a diameter of 2mm to 4mm. The location of the puncture site is near the writ, parallel to the Radius bone.

The insertion is popularly done using the Seldinger Technique. This technique is named after Dr. Sven Ivar Seldinger (1921–1998), a Swedish radiologist who introduced the procedure in 1953
It is used to obtain access safely to blood vessels and other hollow organs through the insertion of a central venous line as well as arterial lines (radial or femoral). The technique uses a hollow needle, exchange wire, and catheter for safe vascular access.

Sheath sizes in Cath lab procedures are-
- Femoral– 4F, 5F, 6F, 7F, 8F, 9F, 10F, 11F, 12F, 14F
- Radial/Ulnar/Brachial– 4F, 5F, 6F
The ‘F’ in the unit place stands for the French scale. It is used to measure the size of the catheter used for the procedure. The size in French units is three times the diameter of the vessel.
Basic Cath Lab Procedures

- CAG (Coronary Angiography) – This procedure is used to diagnose a blockage in coronary arteries. These blockages are formed due to the build-up of plague in the arteries that prevent the optimal supply of oxygen and nutrients to the heart. Detection of blockages can prevent chest pain, ischemic heart disease, and heart attack.
- PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty) – This procedure is used to open up narrowed arteries to reinstate optimal blood flow. The blockage forms due to the deposit of Atherosclerotic Plaque in the coronary arteries.
- PAMI (Primary Angioplasty in Myocardial Infarction) – This procedure is used to open up arteries after blockage due to myocardial infarction. The blockage due to thrombus formed after the heart attack can be effectively removed using PAMI and save life when the patient arrives within one hour (golden hour) of the attack.
- DSA (Digital Subtraction Angiography) – This procedure is used to visualize blood vessels. Angiographic Investigation of this type is done for an accurate visualization of vessels other than coronary arteries.
- EP Study and RF Ablation (Electrophysiology Study & Radiofrequency Ablation) – Electrophysiology study is used to detect arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat) in a patient, manifested by symptoms like rapid heartbeat, fluttering heart, dizziness or shortness of breath. Radiofrequency Ablation is done to correct arrhythmia. A sheath and catheter are used to conduct the process.
- IVUS (Intravascular Ultrasound) – In this procedure, specialized instruments create sound waves inside the lumen of the artery to create an image for visualization. It is most popularly used to access plaque burden inside arteries.
- ROTA (Rotational Atherectomy) – This procedure is used to remove calcified plaque from the arterial walls using high speed rotating burrs. Stenting is done successfully after ROTA.
- FFR (Fractional Flow Reserve) – This procedure compares the real-time blood flow in a patient’s artery to the theoretical value in a normal artery (distal: proximal), thereby diagnosing the presence of blockages.
- Arterial/Ventricular Septal Defects-ASD/VSD/Patent Foramen ovales – PFO / Patent Ductus Arteriosus-PDA – These are minimally invasive procedures to treat congenital heart defects.
- BMV/BAV/BPV (Balloon Mitral Valvotomy) – In this procedure, a balloon-like instrument is used to open up/ expand valves in the heart for optimal flow of blood through the chambers, aorta and arteries.
- Coarctation of the Aorta – This is a congenital defect marked by the narrowing of a section of the aorta. It leads to difficulty in pumping adequate blood through the vessel and requires greater force.
- PPI/ICD/CRT/CRT-D – These are procedures related to Permanent Pacemaker Implant, Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators, Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy with and without Defibrillator.
- TACE (Trans arterial chemoembolization) – This process is used to treat cancer of the liver by embolization (blocking of blood supply) to the tumor site followed by injection of chemotherapy drugs through the same route (hepatic artery).
- UAE (Uterine Artery Embolization) – This procedure is used for the treatment of fibroids (benign tumours) in the uterus without surgery. A catheter is used to deliver embolizing agents in the arteries in the uterus to cut off the blood supply to the fibroids, which, then shrink and die.
- AVI (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation) – This procedure is also referred to as Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR). It is a method of replacement of a diseased valve in the aorta with a new one. It is usually done when the patient suffers from aortic stenosis (stiffness of the valve in aorta, leading to compromised blood flow which might ultimately cause heart failure.
#catheterization #cathlab #cardiology #RadialArtery #CoronaryAngiography #Aneurysm #PseudoAneurysm #intravenouslines #heart #coronary #cardiac #stenosis #aortic
(Disclaimer: Issued in the public interest by Axio Biosolutions Private Limited.)
 A collaborative study with Harvard Medical School
A collaborative study with Harvard Medical School