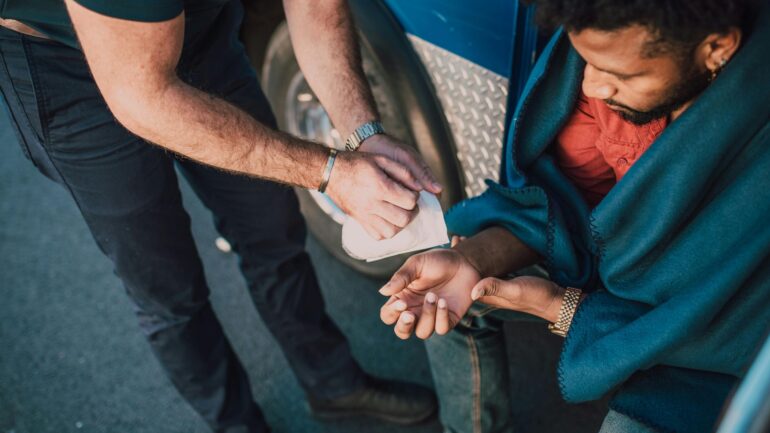
Imagine a crew member aboard the International Space Station accidentally slicing their hand on a sharp instrument—or a naval diver sustaining an injury hundreds of meters below sea level. These are not just theoretical situations but real risks faced during space missions, submarine operations, and high-altitude expeditions.
In such unforgiving environments, effective wound care isn’t optional—it’s a lifeline. These situations are termed as extreme wound care
Space: Wound Care in Zero Gravity
In the microgravity of space, even small wounds can become major complications. Blood does not flow downward but beads and floats, making simple lacerations difficult to manage. Compounding this, astronauts experience:
- A compromised immune system,
- Slower healing, and
- Strict limits on surgical intervention while in orbit.
NASA’s medical protocols exist, but the tools are limited. That’s why wound dressings for space must be:
- Lightweight
- Long-lasting
- Easy to use without water or complex tools
This is where chitosan-based dressings like Axiostat® come into play, offering:
- Rapid haemostasis (fast bleeding control)
- Antimicrobial protection
- Moisture retention (essential in a dry, pressurized cabin)
- Ease of application in low-resource conditions
Importantly, chitosan dressings reduce the need for frequent changes—critical when you’re orbiting 400 km above Earth.
Underwater Missions: The Submarine Scenario
Deep-sea divers and submarine crews face very different wound care challenges. Constrained cabin space, constant humidity, and pressure-related injuries increase infection risks and slow recovery.
In these conditions, antimicrobial and gelling fibre dressings are invaluable as they:
- Minimize bacterial colonization
- Maintain controlled wound moisture
- Manage exudate without damaging surrounding skin
For burns or trauma caused by equipment, cooling gel-based burn dressings combined with antibacterial action can be lifesaving. Chitosan dressings offer a dual advantage: bleeding control plus infection prevention—making them staples in elite diver kits and submarine medical supplies.
High-Altitude and Remote Expedition Care
Now imagine a mountaineer in the Andes suffering a severe laceration—with evacuation days away. Conditions in remote expeditions—whether in the Arctic, jungles, or mountain ranges—make wound management even more critical:
- Harsh temperatures
- Non-sterile environments
- Limited medical expertise
The greatest danger in such settings is traumatic blood loss, which rapidly induces hypothermia. Cold blood reduces platelet function and coagulation activity, making clotting extremely difficult.
Here, chitosan-based hemostats like Axiostat® prove lifesaving. Used by the Indian Army in Siachen Glacier, Dras Valley, and Ladakh, these products remain effective under extreme cold because:
- The charge-based interaction between chitosan and blood is not affected by temperature.
- At the molecular level, Axiostat® activates platelets through TLR pathways, triggering Factor X activation and stable clot formation—even in hypothermia.
Why This Matters for Civilian and Military Use
While these extreme scenarios highlight the limits of human endurance, the solutions developed extend far beyond space, submarines, and glaciers.
The same chitosan dressings that stop bleeding in orbit are now integral to:
- Battlefield trauma kits
- Coast guard emergency packs
- Adventure travel and mountaineering first-aid kits
For soldiers, medics, and civilians alike, reliability under pressure is non-negotiable. Durable, multifunctional dressings like Axiostat® ensure survival in places where help may never arrive in time.
Conclusion
Wound care in extreme environments is not about convenience—it’s about survival. By adopting innovations like chitosan wound dressings, we are better prepared to save lives in the harshest conditions on Earth—and even beyond it.
So whether you’re preparing for a spacewalk, a submarine dive, or a solo trek across the Himalayas, remember: your first-aid kit should carry innovation, not just hope.
 A collaborative study with Harvard Medical School
A collaborative study with Harvard Medical School