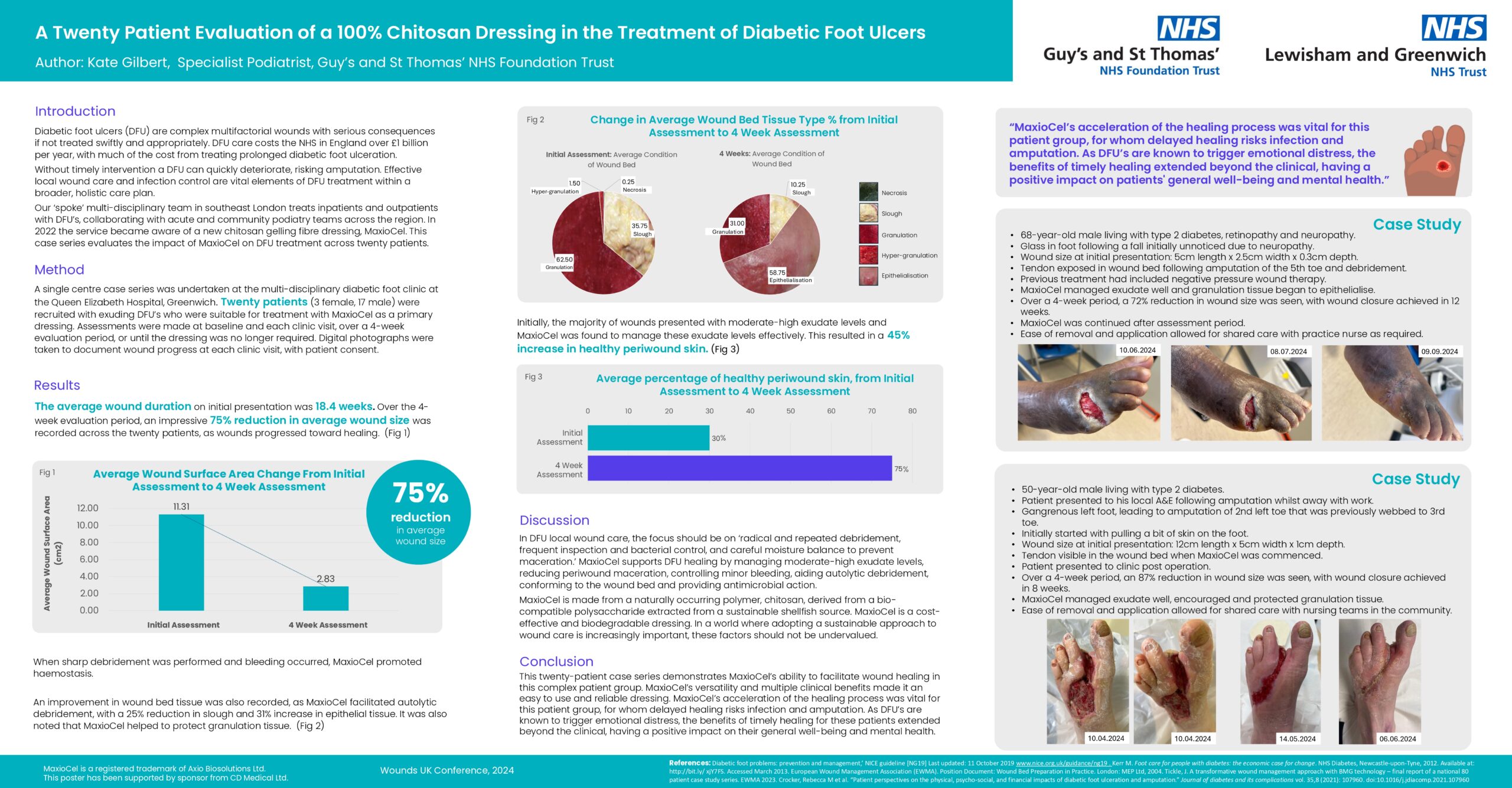
Evaluation of Chitosan-Based Axiostat as Hemostatic Dressing for Endovascular Procedures in Patients with Leriche Syndrome on Anticoagulant Therapy
Publication Details:
Perri, P.; Curcio, F.; De Luca, M.; Piro, P.; Trombino, S.; Cassano, R. (2025) Evaluation of Chitosan-Based Axiostat as Hemostatic Dressing for Endovascular Procedures in Patients with Leriche Syndrome on Anticoagulant Therapy. Pharmaceuticals, 18(4), 584.
Access-Site & Patient Cohort
This retrospective, single-center study (Sep 2022–Feb 2024) assessed 60 consecutive patients (mean age 67.4 ± 2.8 yrs; 40% M/60% F) undergoing axillary arterial access for endovascular treatment of Leriche syndrome, all managed with manual compression aided by Axiostat, a 100% chitosan hemostatic dressing.
| Variable | All Patients (N = 60) |
| Age (years) | 67 ± 2.8 (mean 67.4) |
| Sex | 40% M / 60% F |
| Body Mass Index* | 27 ± 0.7 (mean 27.1) |
| aPTT** (seconds) | 33 ± 0.8 (mean 33.2) |
| Platelet Count (×10⁶/mL) | 330 ± 8.7 (mean 330.6) |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 40 pts (66%) |
| Hypertension | 33 pts (56%) |
| Coronary Artery Disease | 8 pts (13%) |
| Smoking History | 45 pts (75%) |
Procedural & Pharmacologic Details
All patients underwent axillary access with predominantly 6 Fr or 8 Fr introducer sheaths (mean punctures 1.2 ± 0.2), without suspending pre-existing antithrombotic regimens.Baseline INR averaged 1.3 ± 0.2, confirming safe continuation of anticoagulation during access site management.
Efficacy, Safety & Follow-Up
Primary technical success (hemostasis within 10 min without re-compression) was 100% for antiaggregant‐only patients and 95–98% in anticoagulated cohorts. Secondary technical, clinical and surgical success rates were ≥ 96% across all groups. All patients mobilized within 24 h, and 99.9% achieved complete axillary-site healing by Day 30.
| Outcome | Mono-Antiagg. | Dual-Antiagg. | Anticoagulant | Combo (Antiagg.+Anticoag.) |
| Primary Success (%) | 100 | 100 | 98 | 95.5 |
| Secondary Technical (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Clinical Success (%) | 100 | 100 | 98 | 96 |
| Ambulation at 24 h (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Healing at 30 days (%) | 100 | 100 | 98.8 | 96 |
Complication rate was low (1.8% hematoma; 2.9% pseudoaneurysm; 1.2% required surgical repair), with no cases of dissection or arteriovenous fistula formation.
Hemostasis Performance
Hemostatic success at 10 min was 99.5% overall; median time to achieve hemostasis was 5.75 min (range 5–7 min depending on therapy). Failure cases occurred primarily in dual antiplatelet or anticoagulant patients, likely due to higher blood flow delaying clot formation.
Group | Success (%) | Time to Hemostasis (min) | Failure (%) |
Mono-antiaggregant therapy | 100 | 5 | 0 |
Dual-antiaggregant therapy | 100 | 6 | 0 |
Anticoagulant therapy | 99.5 | 5 | 0 |
Antiaggregant + anticoagulant | 98.2 | 7 | 1.8 |
Effect on Access-Site Management
Axiostat’s cationic chitosan matrix forms an immediate mucoadhesive barrier and promotes rapid fibrin plug formation under manual compression, even in coagulopathic patients. Its porous structure interlocks with tissue, enabling consistent hemostasis without interrupting antithrombotic therapy.
Key Insights:
- Rapid Hemostasis: Median time < 6 min with > 99% success, minimizing bleeding complications in anticoagulated patients.
- Therapy Compatibility: Safe application without halting antiplatelets/anticoagulants, preserving therapeutic INR levels.
- Low Complication Profile: Rare hematomas/pseudoaneurysms and minimal need for surgical intervention.
- Ease of Use: Simple manual compression protocol with atraumatic removal via saline irrigation.
Axiostat® is a registered medical device of Axio Biosolutions Pvt. Ltd.
 A collaborative study with Harvard Medical School
A collaborative study with Harvard Medical School