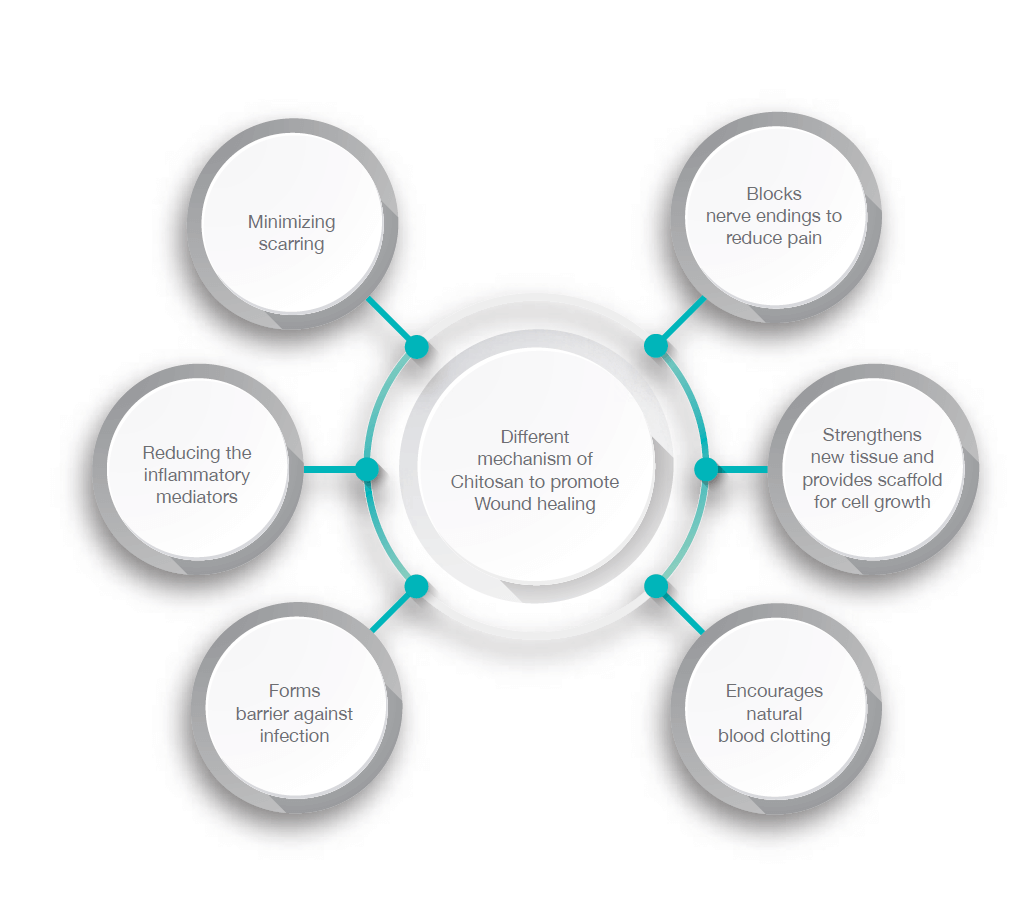
Wound Healing Properties
Chitosan assists in the wound healing process in every stage through various ways such as;
- Hemostasis
- Re-epithelization of skin
- Macrophage activation followed by anti-inflammatory
- Pain reduction
- Inhibition of metalloproteinase-2
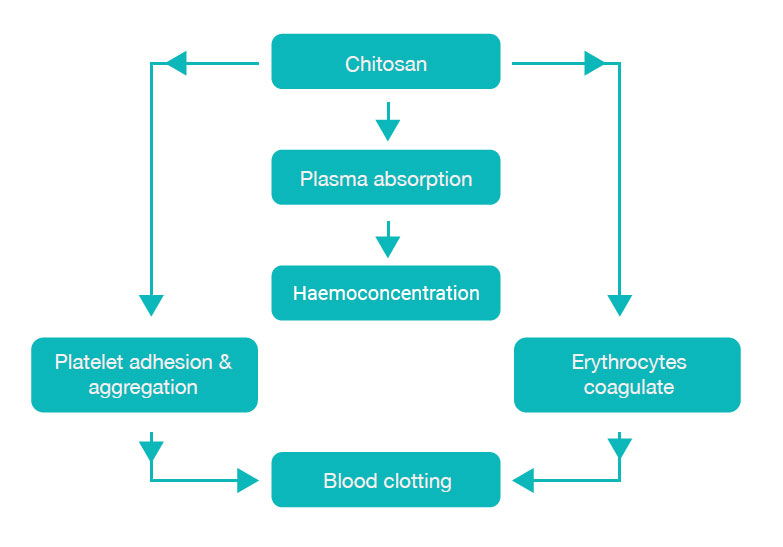
Mechanism of Haemostatic Action
- Fluid absorption capacity: 30 times the weight of dressing
- Once absorbed the exudate is locked within the fibers of the dressing
- The gelling fibers prevent wicking of exudate into surrounding skin
Dispersion Test & Wet Strength
Wet strength of Maxiocel is around 3 times greater than the traditional gelling fiber dressing. Its outstanding strength makes it
- Intact during dressing change for a longer time
- Painless easy removal from the wound surface

SEM Images of chitosan and RBC interaction
SEM Images of chitosan and platelet interaction
Re-Ephithilazation
Mechanism of Action:
- Chitosan stimulates the proliferation of dermal fibroblast and allows the fibrous tissue formation
- Chitosan interacts with growth factors of serum and metal ions such as calcium that induce rapid proliferation of fibroblast
- Chitosan inhibits the proliferation of keratinocytes
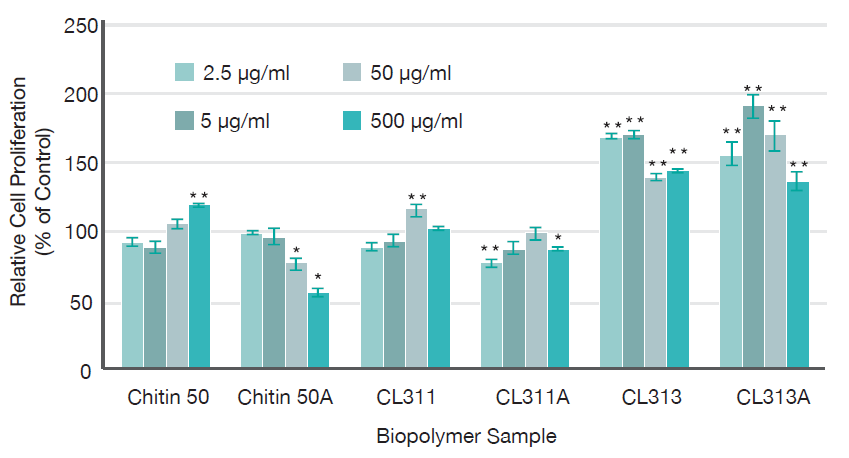
Initial screening of chitin/chitosan samples for effect on “fibroblast proliferation in vitro. Human dermal “fibroblasts (C520) were treated with various chitosan samples for 3 days. The 3H thymidine cell proliferation assay was then performed. Data (n=3 ±SEM) are presented as percentage of the controls (no polymer present) (*P (0.05, **P (0.01, ANOVA).
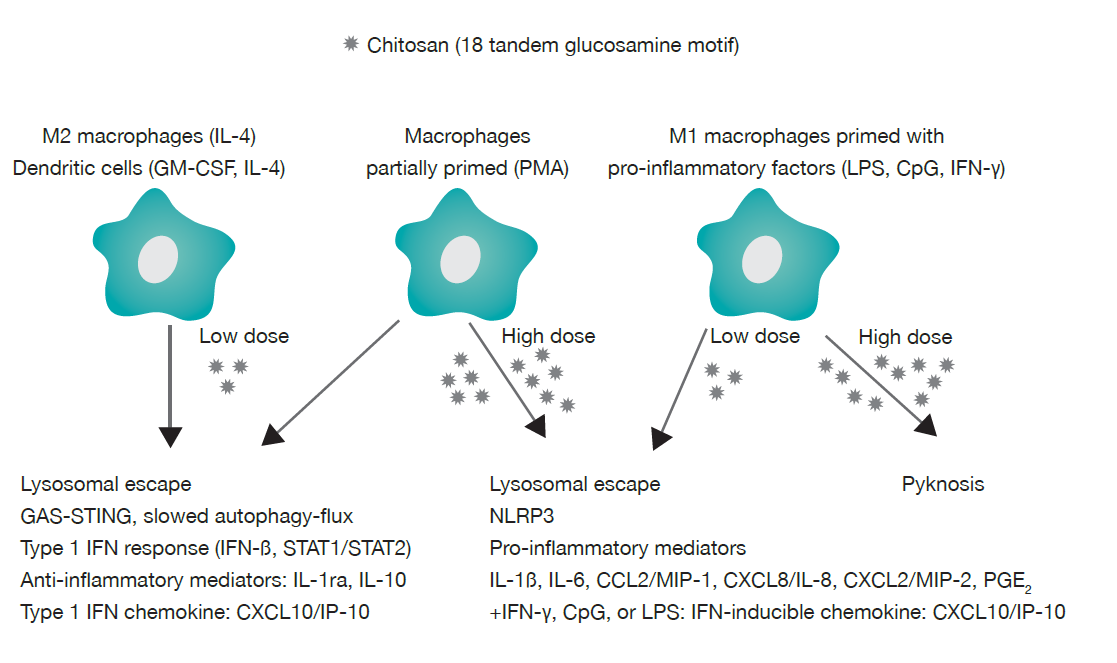
Anti-Inflammatory Property
Mechanism of Anti-inflammatory Action:
- Chitosan produce significant inhibition effect against inflammation mediator such as Interleukin (IL)- 2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10
and IL-13. - Chitosan causes the reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α
- Chitosan suppress the NF-kβ expression and AP-1 activation
Inhibitory Effect Of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2
Mechanism of Action for MMP-2 inhibition:
- MMP-2 cause digestion of extracellular matrix of skin that delayed the wound healing process. Chitosan strongly inhibit
the activation and expression of MMP-2 in human dermal fibroblast. - Chitosan inhibit the TNF-α factor that helps in the expression of MMP-2
- Chelating ability of chitosan with Zn+2 which is a vital factor for MMP-2 activation
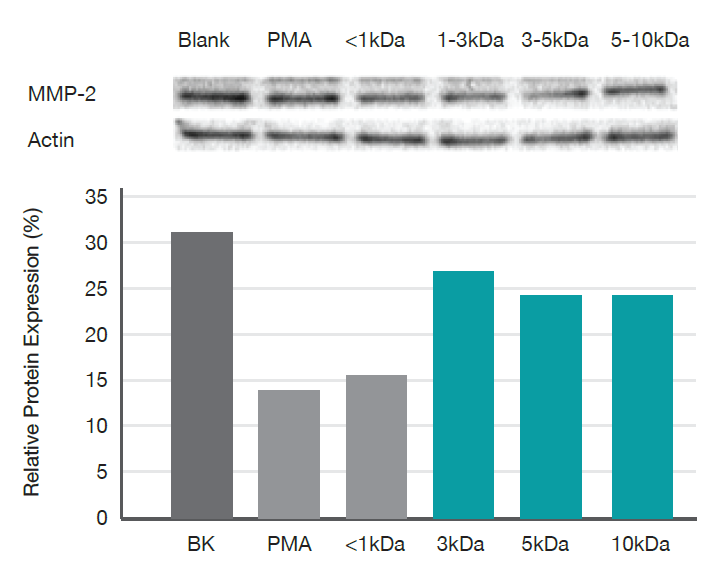
Western blot analysis of protein expression of proMMP-2 in HDFs after
treatment with different molecular weights of Chitosan molecule. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) treatment significantly increased the expression level of MMP-2 protein compared to blank group. The expression level of MMP-2 significantly (P<0.01) decreased with the treatment of chitosan for all molecular weight.
Scar Prevention Activity
Mechanism of Scar Prevention:
- Chitosan gradually depolymerize into N-acetyl-b-D-glucosamine, which initiates hyaluronic acid synthesis at the wound site that helps in faster scar improvement.
- In the presence of chitosan, type IV collagen produced in the form of fine reticulin like fibrils rather than mature bands of dense collagen which leads to scarring
- Chitosan significantly decrease the expression of TGF-β1 factor by blocking the cyclooxygenase and arachidonic acid pathway that improve the scar part.

After 21 days, wound surface with Control
(Cotton gauze)

After 21 days, wound surface showed
scar improvement with Chitosan dressing
 A collaborative study with Harvard Medical School
A collaborative study with Harvard Medical School