The Role of a Chitosan BMG™ Dressing in Managing a Static Surgical head Wound
Publication Details:
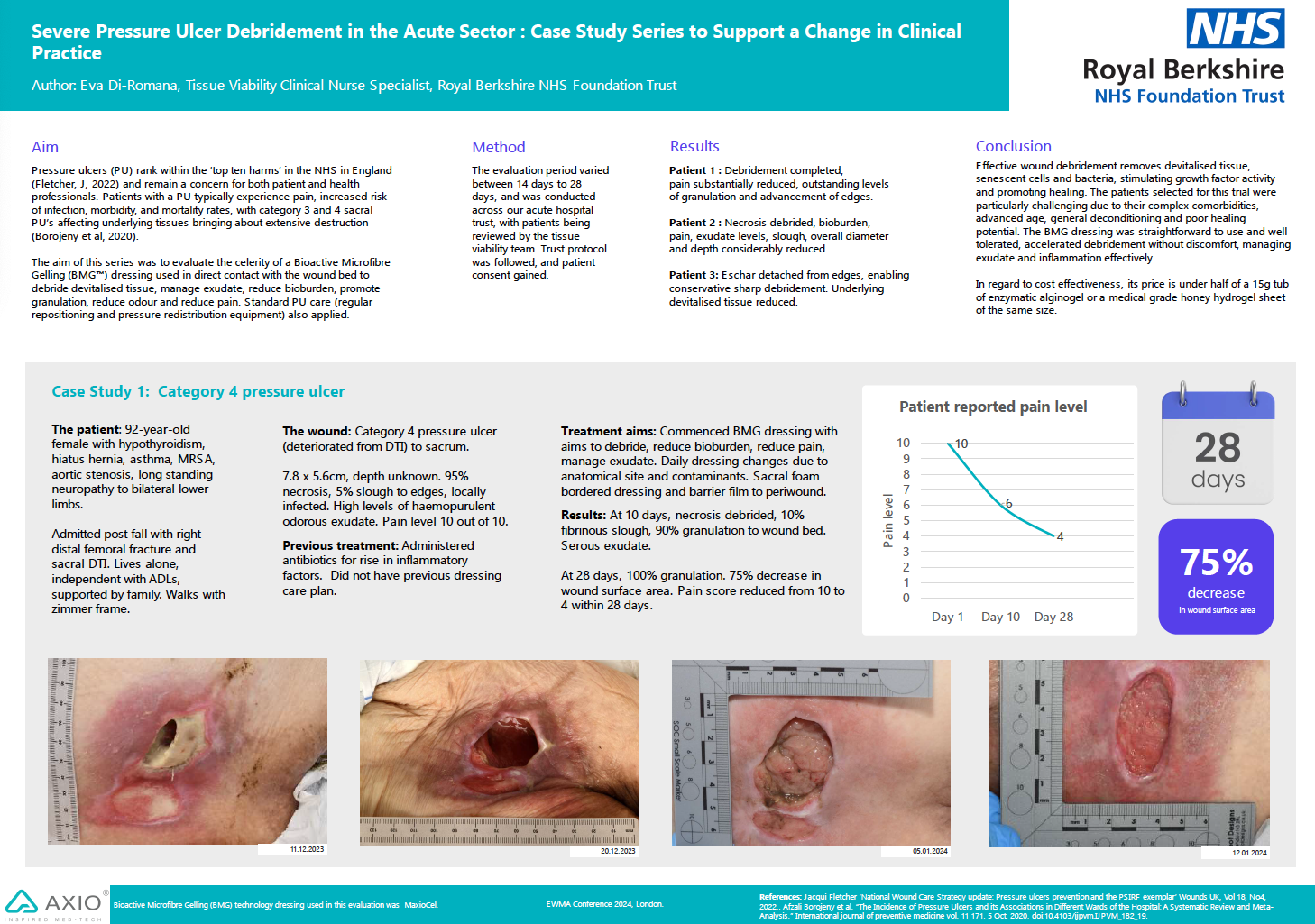
Jackson, E. & Varnam, K. (2025) The role of a chitosan BMG™ dressing in managing a surgical head wound: A case study on healing, wellbeing, and self-care. Wound Care Today, 2025.
Wound Details
A 74-year-old female with a 12-month-old static surgical wound (3 × 3 cm) on the forehead, previously unresponsive to various dressings.
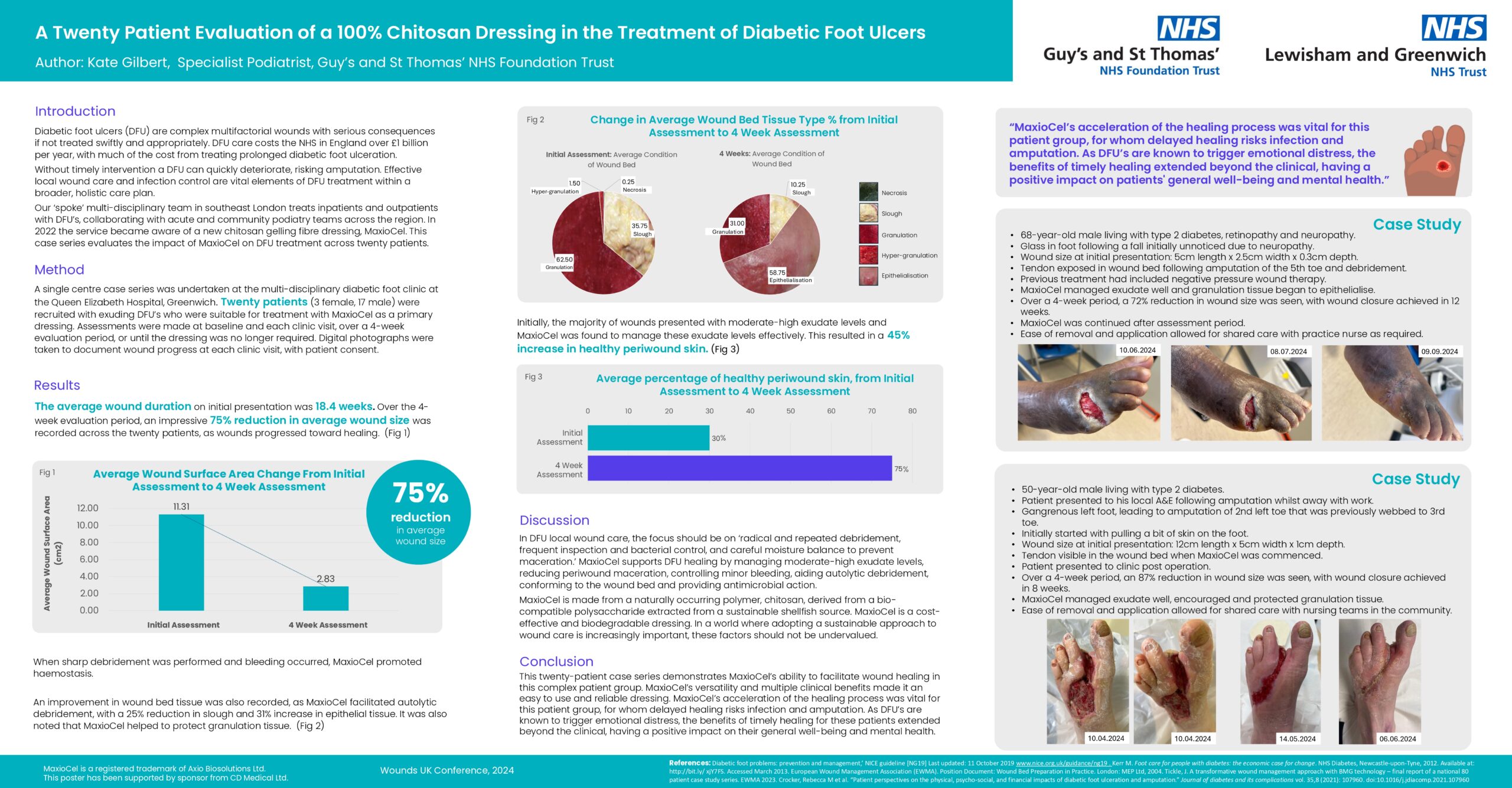
Key Findings and Data:
Measure | Baseline | After 4 Weeks |
Wound Size | 3 × 3 cm (100% granulation) | 0.8 × 1 cm (91% reduction) |
Peri-wound Condition | Dry, eczematous | Healthy |
Patient-reported QoL | High anxiety about appearance | Increased confidence; resumed social activities |
Self-care Ability | Fully nurse-dependent | Independent dressing changes by Week 3; able to wash hair after 12 months |
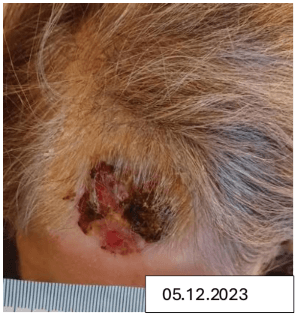
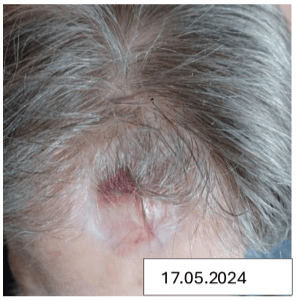
Effect on Wound Bed and Management:
- Granulation & Contraction: Rapid wound contraction (91%), with the wound fully healed by Week 23 post-evaluation.
- Skin Restoration: Peri-wound skin transformed from eczematous to healthy.
Clinician and Patient Feedback:
- Clinicians: Praised the dressing’s ease of application/removal and its capacity to enable self-care.
- Patient: Reported reduced anxiety, improved confidence in appearance, and joy at regaining hair-washing ability.
Key Insights:
- MaxioCel dressing not only accelerates healing of static surgical wounds but also significantly enhances patient wellbeing and autonomy.
- Supported self-care reduces nursing interventions and fosters patient empowerment in community settings.
 A collaborative study with Harvard Medical School
A collaborative study with Harvard Medical School